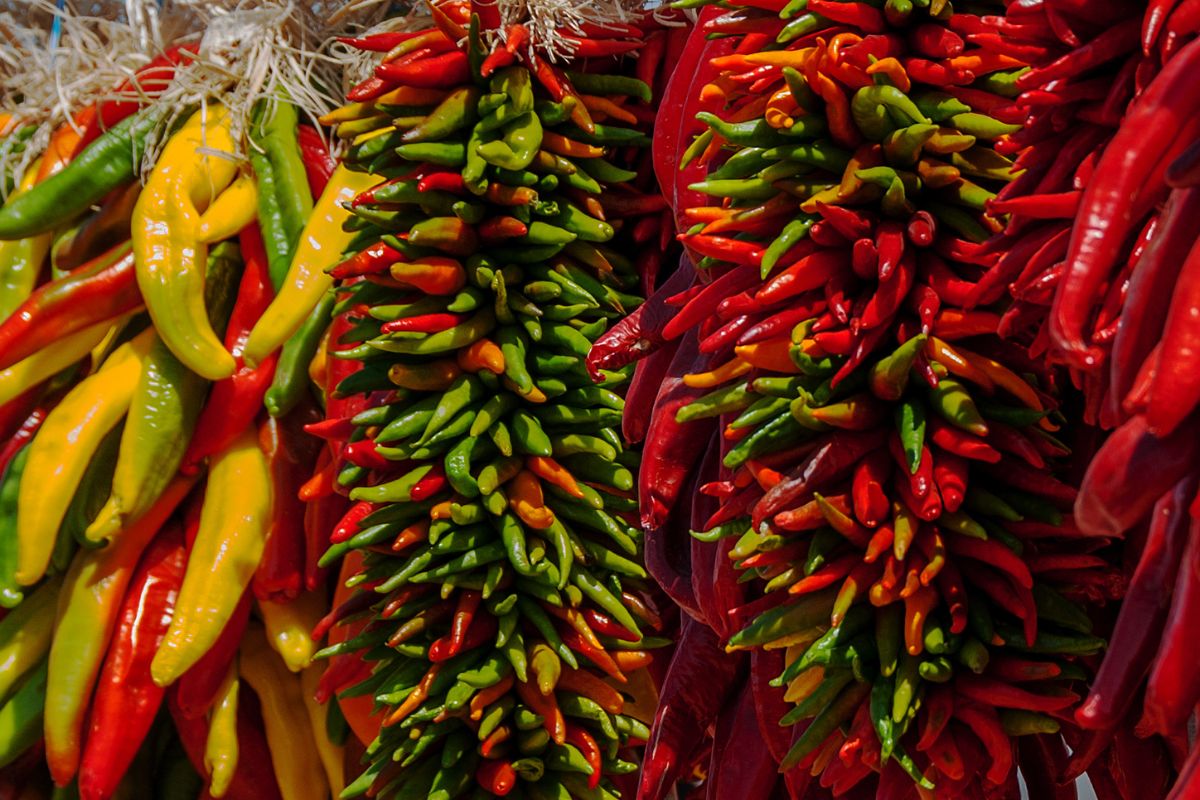
New Mexico chile pods are chili peppers cultivated mainly in the New Mexico state. They offer an earthy and slightly sweet flavor to recipes, and they also come with dried cherry undertones and crisp acidity. Cooks typically make an enchilada sauce with them.
Table of Contents
What are the new mexico chile pods?
New Mexico chile pods are the best-known crop of New Mexico, and they’ve been cultivated in the Rio Grande Valley for about four centuries.
They are a product of years of breeding and cultivar development and are said to be descendants of Central Mexico chiles.
Why are they called New Mexico chile pods?
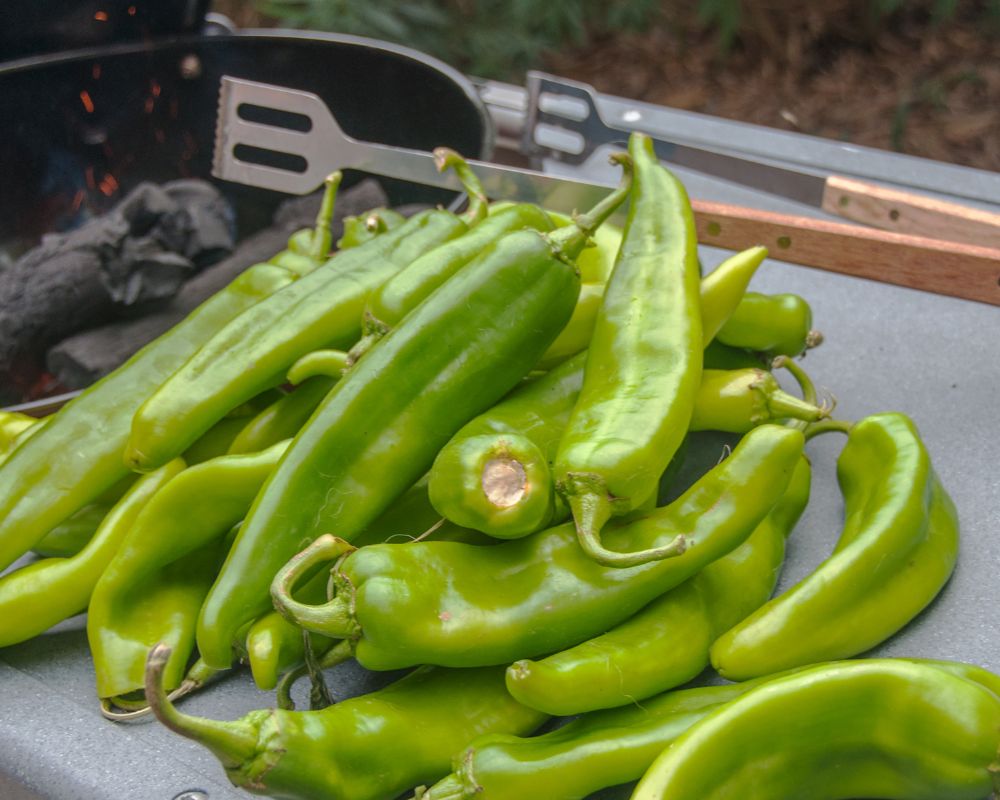

New Mexico chile is an all-encompassing term referring to chiles grown in various regions across the state.
Hatch chile, a variety specifically grown in the Hatch Valley; green chile, chile in its fresh form; and red chile or ripened chile, all belong to this classification.
| Origin | Developed in the New Mexico State University (NMSU) |
| Appearance | Fresh peppers are slender and green, dark red when ripe |
| Flavor profile | Complex flavor profile, smoky |
| Heat level | 800 – 1,400 SHU |
Origin
New Mexico chile pods (Chile Nuevo Mexico Entero) are botanically classified as Capsicum annuum.
The New Mexico State University (NMSU) developed these chiles from chile pepper varieties indigent to Central Mexico. NMSU’s first horticulturist, Dr. Fabian Garcia, bred chiles and created the so-called New Mexico No. 9, a descendant of chile pasilla, chile negro, and chile Colorado.
Today, people use these chile pods fresh or dry in various cuisines, notably Tex-Mex and Southwestern. El Guapo, a leading brand in the culinary world, offers a range of these chiles as a whole, chile molido, and chile powder.
Appearance
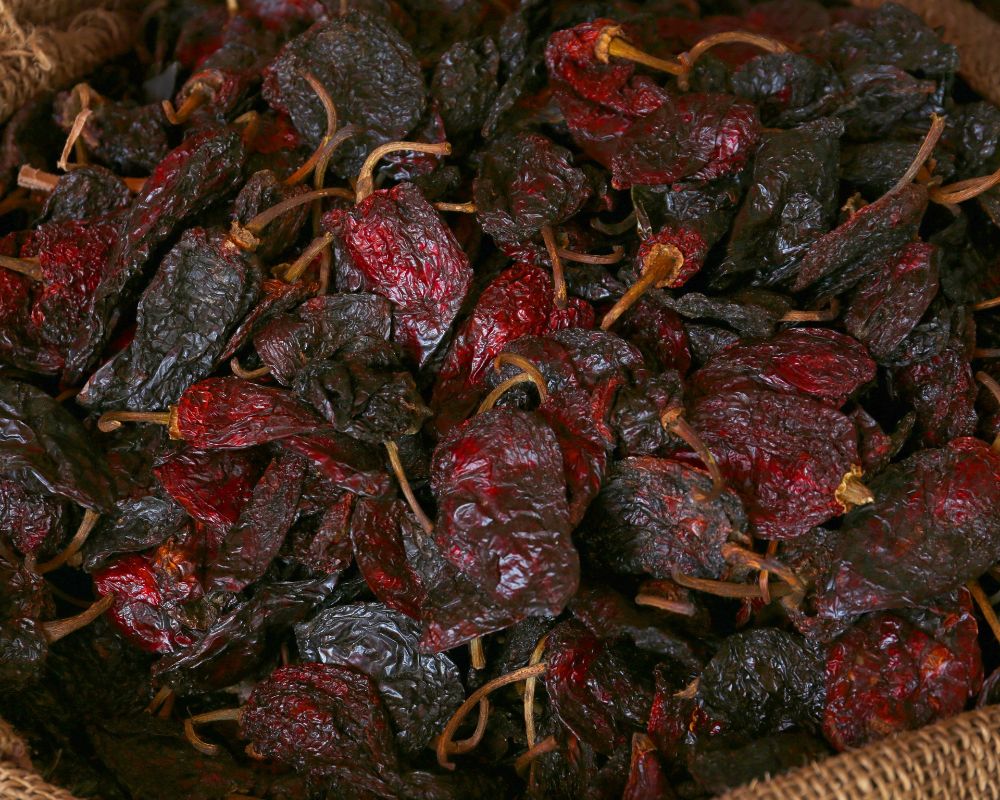
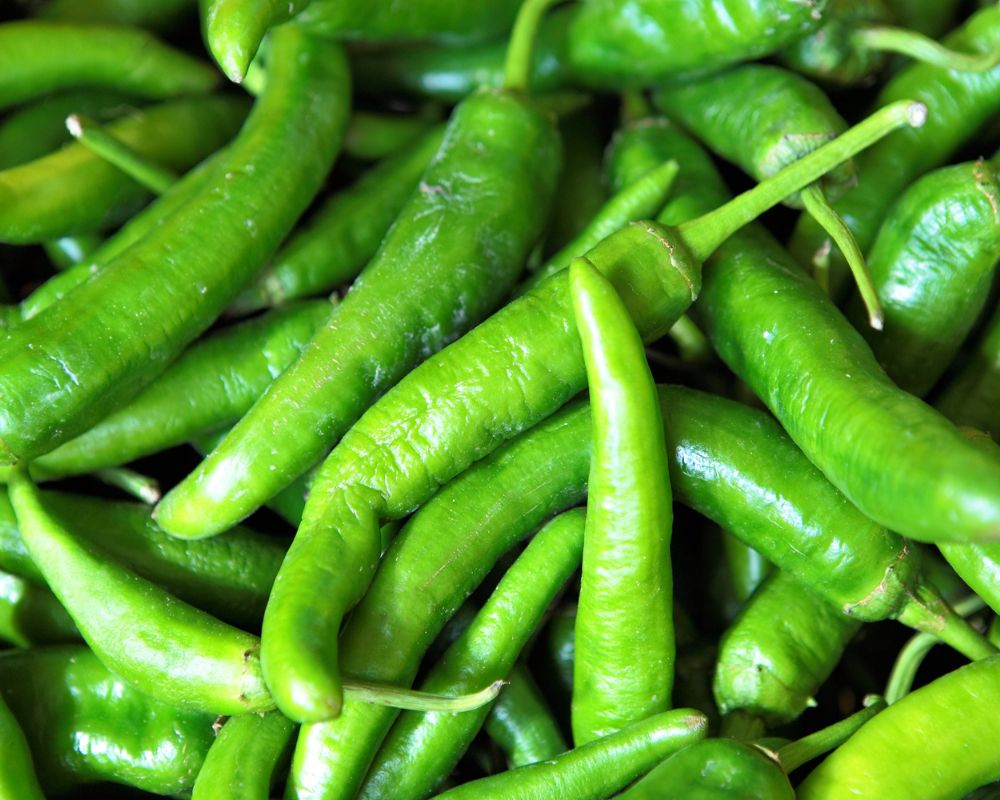
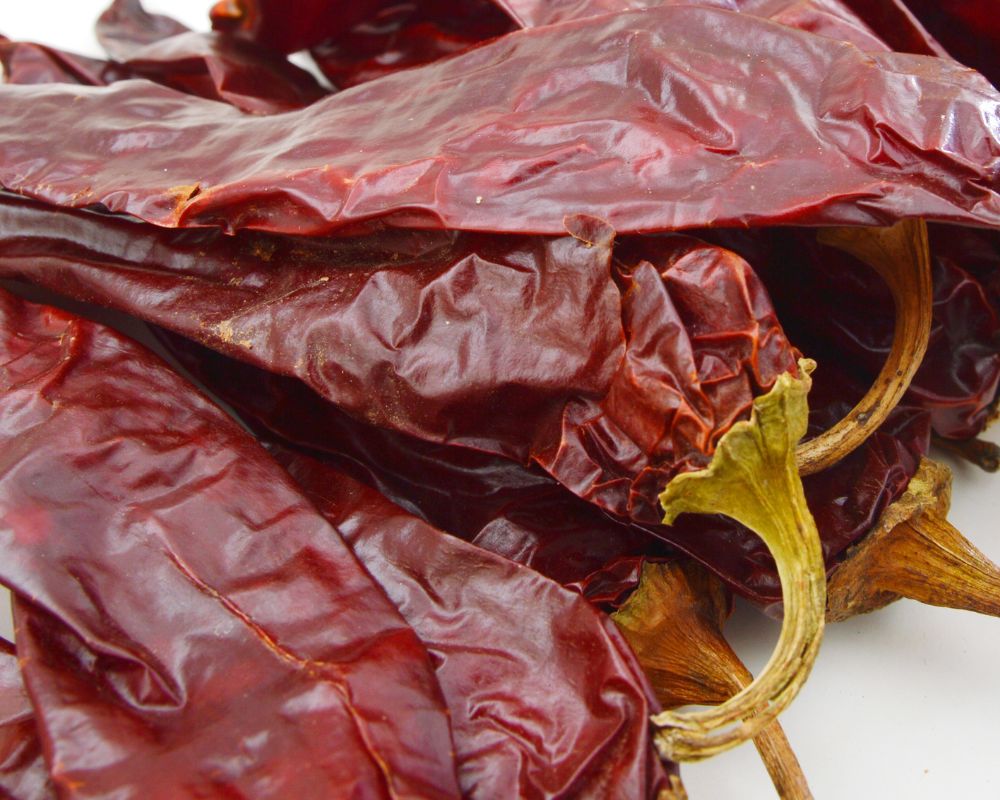
New Mexico chile peppers are slender and green when fresh. As they ripen, they become dark red.
When sun-dried or dried in any other method, these chiles become flat and tapered, with smooth, glossy skin featuring deep wrinkles and folds. Inside, you’ll find golden yellow seeds filling the hollow interior.
Flavor profile
New Mexico chiles enrich recipes with a subtly sweet and intense flavor and aroma.
Green ones have a particularly smoky taste. Meanwhile, dried red chile pods retain the same flavor profile but with the addition of some earthiness. They also have crisp acidity and dried cherry undertones.
Heat Level
These chili peppers boast mild and slow-building heat, with 800 to 1,400 Scoville heat units (SHU).
They are hotter than California chiles (which come at 500 to 1,000 SHU) but are milder than guajillo (2,500 to 5,000 SHU) and Chile de arbol (15,000 to 30,000 SHU).
Nutritional Benefits of new mexico chile pods

According to this nutritional information from NMSU, these chili peppers have:
- Calcium
- Iron
- Magnesium
- Phosphorus
- Potassium
- Vitamins A, C, B2, and B6
These vitamins and minerals help boost the immune system and support healthy bodily functions.
Additionally, the capsaicin that it contains has anti-inflammatory properties. Manufacturers extract them to produce topical pain relievers.
What recipes call for new mexico chile pods?
Apart from Tex-Mex and Southwestern cuisines, these chile pods are essential to Asian, Caribbean, Indian, and American culinary practices. You can use them to pack a subtle heat and add depth and flavor to recipes such as soups, salsas, stews, marinades, and sauces (including enchilada sauce).
The culinary application will also depend on the kind of chile pepper you have. For example, you can best use green chiles to make a cream of green chile soup. If you have a New Mexico red chile supply, you can use these red chili pods for cooking chicken enchilada with red chile sauce. You can also prepare red chile pork stew or a red chipotle sauce, which is great for tortillas.
When minced, you can use dried chile peppers to season rice-based dishes and stir-fried. When ground, you can sprinkle it onto pizza and casseroles. You can also combine them with other spice rubs and use the blend to add flavor to meat dishes. As a versatile flavoring tool, New Mexico chiles work well with poultry, beef, and fish.
A recipe I recommend: New Mexico Red Chile Sauce
What do I need to make New Mexico chile pods?
You will need New Mexico chili peppers seeds and a warm, sunny place. Harvest them green or red within 65 to 120 days.
To dry red chiles, simply hang them in a place with low moisture and where the sun reaches them. To use them as a ground spice, lightly toast them over medium heat and grind them in a processor or blender.
What can I use instead of New Mexico Chile pods?



If you don’t have New Mexico chile pods, you may find it hard to replicate their complex flavor. Still, you can try these substitutes:
- Ancho chiles
- California chiles
- Guajillo
Ancho chiles are large chiles that have a dark mahogany color. Available as fresh or dried chiles, they impart a fruity flavor to recipes. They are also hotter than New Mexico chiles.
California chiles, as stated, have a milder heat. They resemble chile guajillo in appearance: long, shiny, and red. You can use them as a swap for New Mexico chili peppers because of their smoky and earthy flavor profile that comes with tangy and fruity undertones.
You can count on guajillo as a replacement if you want more heat. These chiles are subtly fruity with hints of smokiness, pine, and tart berries.